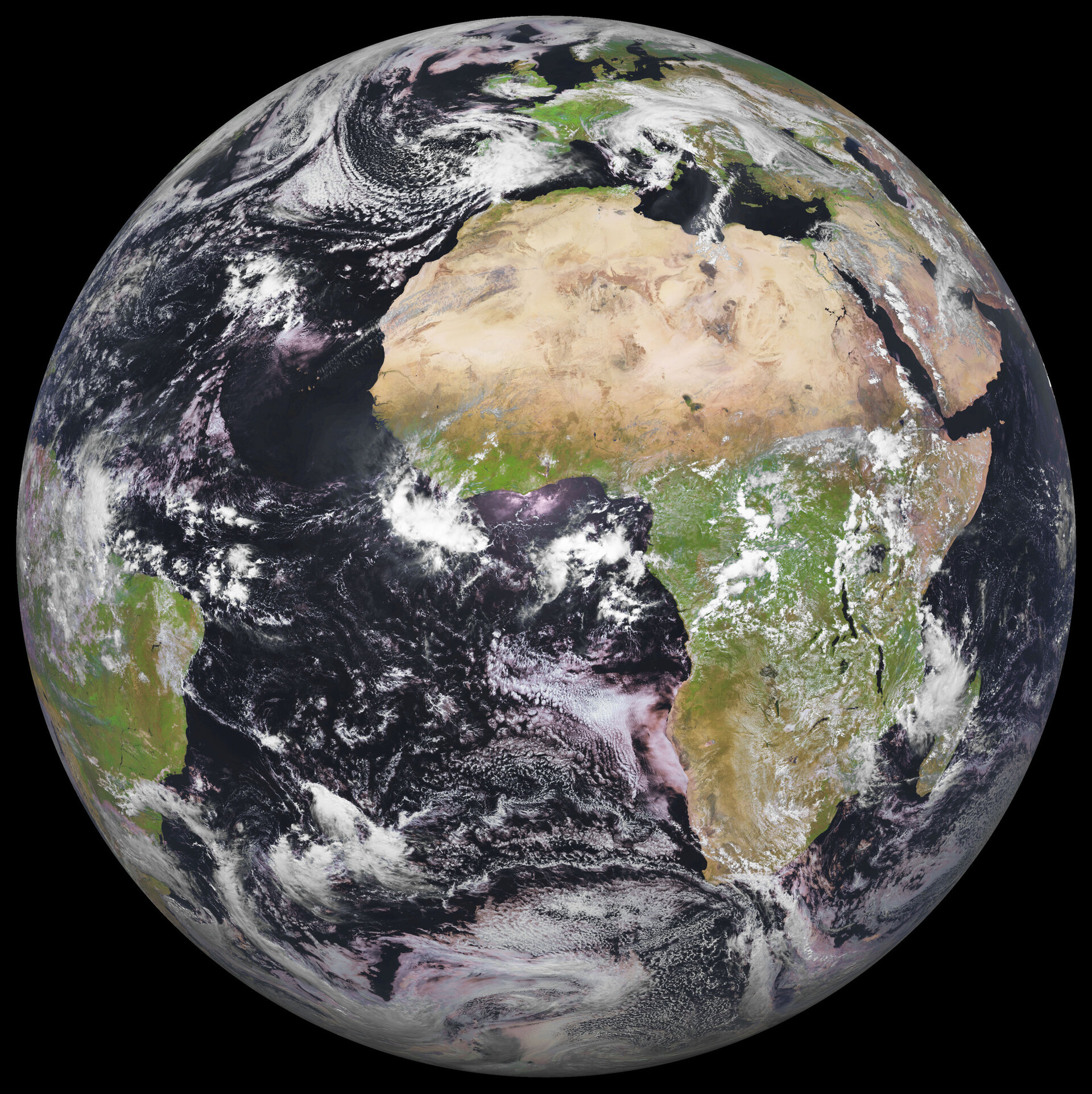
Earth, our home planet, holds countless mysteries and wonders waiting to be discovered. From its breathtaking landscapes to its diverse ecosystems, it is a marvel that continues to inspire and astonish scientists and explorers alike. Understanding Earth's complexities is crucial for our survival and the preservation of its beauty.
As we delve into the fascinating world of Earth, we uncover its intricate systems, geological formations, and the delicate balance that sustains life. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of our planet, offering valuable insights and knowledge to readers eager to learn more about the world around them.
By the end of this article, you will gain a deeper appreciation for Earth's wonders, its challenges, and the importance of conservation efforts. Let’s embark on this journey together and uncover the secrets of the planet we call home.
Read also:Will Smith Sister Ashley A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life And Influence
Table of Contents
- Geography of Earth
- Climate and Weather Patterns
- Biodiversity and Ecosystems
- Human Impact on Earth
- Natural Wonders of Earth
- Conservation Efforts
- Earth's Natural Resources
- Earth in Space
- Scientific Discoveries About Earth
- The Future of Earth
Geography of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only known celestial body to support life. Its geography is incredibly diverse, featuring vast oceans, towering mountains, sprawling deserts, and lush forests. Understanding Earth's geography is essential for comprehending the planet's natural processes and human interactions.
Major Landforms
Earth’s surface is composed of various landforms, each playing a unique role in the planet's ecosystem. Below are some of the most prominent landforms:
- Mountains: These elevated landforms are formed through tectonic activity and erosion. Examples include the Himalayas and the Andes.
- Plains: Flat, low-lying areas that cover large portions of Earth's surface. The Great Plains in North America is a notable example.
- Valleys: Depressions between mountains or hills, often carved by rivers. The Grand Canyon is one of the most famous valleys.
Oceans and Water Bodies
Water covers approximately 71% of Earth's surface, making oceans a critical component of the planet's geography. The five major oceans are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. These water bodies regulate climate, support marine life, and provide resources for human use.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Earth's climate is a dynamic system influenced by various factors, including solar radiation, atmospheric composition, and ocean currents. Understanding climate patterns is vital for predicting weather changes and mitigating their impacts.
Types of Climates
Earth exhibits a wide range of climates, from tropical rainforests to polar ice caps. The Köppen climate classification system categorizes climates into five main types:
- Tropical: Characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall.
- Desert: Arid regions with minimal precipitation.
- Temperate: Moderate climates with distinct seasons.
- Continental: Cold winters and hot summers.
- Polar: Extremely cold climates with ice-covered surfaces.
Weather Patterns
Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation. Weather patterns are influenced by factors like air pressure, wind, and moisture. Meteorologists use advanced technology to monitor and forecast weather changes, helping communities prepare for natural disasters like hurricanes and tornadoes.
Read also:Sydney Sweeneys Role In The Handmaids Tale A Deep Dive Into Her Impact And Performance
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. From microscopic organisms to large mammals, every species plays a role in the planet's ecological balance.
Types of Ecosystems
Ecosystems are communities of living organisms interacting with their physical environment. Examples include:
- Forests: Home to a wide range of plant and animal species.
- Grasslands: Dominated by grasses and supporting diverse wildlife.
- Wetlands: Areas where water saturates the soil, providing habitats for water-dependent species.
Threats to Biodiversity
Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change, pose significant threats to biodiversity. Protecting ecosystems and preserving endangered species is crucial for maintaining Earth's ecological balance.
Human Impact on Earth
Human activities have a profound impact on Earth's environment, both positive and negative. Industrialization, urbanization, and technological advancements have transformed the planet, often at the expense of natural resources.
Environmental Challenges
Some of the most pressing environmental challenges include:
- Climate change: Rising global temperatures and its consequences.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil contamination from human activities.
- Deforestation: Destruction of forests for agriculture and urban development.
Sustainable Practices
Adopting sustainable practices is essential for mitigating the negative impacts of human activities. Renewable energy, waste reduction, and conservation efforts are some of the solutions being implemented worldwide.
Natural Wonders of Earth
Earth is home to numerous natural wonders that showcase the planet's beauty and complexity. From the Great Barrier Reef in Australia to the Aurora Borealis in the Arctic, these marvels inspire awe and wonder.
Geological Wonders
Geological formations, such as the Grand Canyon and Mount Everest, are testaments to Earth's geological history. These landmarks attract millions of visitors each year, contributing to local economies and cultural heritage.
Biological Wonders
The diversity of life on Earth is another source of amazement. Coral reefs, rainforests, and mangroves are examples of biological wonders that support countless species and provide essential ecosystem services.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation is the practice of protecting Earth's natural resources and biodiversity. Governments, organizations, and individuals worldwide are working together to preserve the planet's ecological integrity.
Protected Areas
Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, is a key strategy for conservation. These areas safeguard habitats and species from human interference and degradation.
Community Involvement
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for their success. Education, awareness campaigns, and participatory programs empower people to take action and protect their environment.
Earth's Natural Resources
Earth provides a wealth of natural resources essential for human survival and economic development. These resources include water, minerals, forests, and fossil fuels. However, overexploitation and mismanagement threaten their sustainability.
Sustainable Resource Management
Implementing sustainable resource management practices ensures the long-term availability of natural resources. Techniques such as reforestation, water conservation, and renewable energy development are being adopted globally.
Earth in Space
Earth's position in the solar system and its interactions with other celestial bodies influence its environment and climate. Studying Earth from space provides valuable insights into its systems and processes.
Satellite Technology
Satellites play a crucial role in monitoring Earth's climate, weather patterns, and natural disasters. They provide real-time data that helps scientists and policymakers make informed decisions.
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is the study of life beyond Earth and its potential implications for our planet. Exploring other planets and moons in our solar system may reveal clues about Earth's origins and future.
Scientific Discoveries About Earth
Scientific research has significantly advanced our understanding of Earth. From plate tectonics to climate science, discoveries continue to shape our knowledge of the planet.
Plate Tectonics
The theory of plate tectonics explains the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates and their role in shaping the planet's surface. This discovery revolutionized geology and provided insights into earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain formation.
Climate Science
Climate science investigates Earth's climate system and its responses to natural and human-induced changes. Advances in this field have improved our ability to predict and mitigate climate-related risks.
The Future of Earth
The future of Earth depends on the choices we make today. Addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainable development are essential for ensuring a livable planet for future generations.
Technological Innovations
Innovations in technology offer promising solutions to environmental problems. Advances in renewable energy, carbon capture, and waste management are being developed to reduce humanity's ecological footprint.
Global Cooperation
Global cooperation is crucial for tackling Earth's challenges. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, demonstrate the commitment of nations to work together for a sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Earth is a remarkable planet with a complex and interconnected system of natural processes. Understanding its geography, climate, biodiversity, and human impact is essential for preserving its beauty and ensuring its sustainability. By adopting sustainable practices and promoting global cooperation, we can create a better future for all.
We invite you to take action by sharing this article, exploring related topics, and joining the conversation on Earth's preservation. Together, we can make a difference and protect the planet we call home.